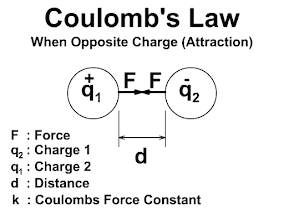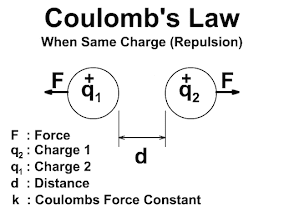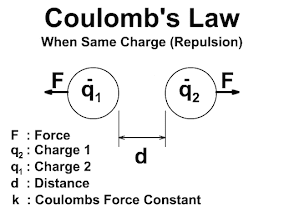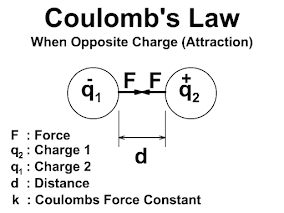
DARLINGTON TRANSISTOR
A Darlington transistor circuit is a combination of two bipolar transistors connected in such a way as to provide a high current gain. Advantages: High current gain High input impedance High voltage amplification Drawbacks: High voltage drop High power dissipation High thermal resistance Applications: Power amplification Motor control High voltage switching Challenges: Heat dissipation Stability of the circuit Numerical: High current gain: typically 1000 or more Formula: Common emitter current gain (beta) of Darlington transistor circuit = β1 * β2, where β1 and β2 are the current gains of the individual transistors. Derivation: Darlington transistor circuit is derived from the basic bipolar transistor configuration. Frequency range: The frequency range of Darlington transistor circuit depends on the individual transistors used and can range from a few Hz to several MHz. Year of discovery: Darlington transistor was invented by Sidney Darlington in 1953. Waveform: The waveform of Darli